Checking the status of your jobs
So you’ve launched a job, yay!
Let’s look at some ways to look at the status of your job, check activity across the cluster, and delete a job.
Slurm: squeue
Running squeue (think: Slurm queue) from your terminal on a front-end will give you a table of statistics about all of the jobs currently running on that sub-cluster. The output will look like:
12 [bora] squeue
JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
4114 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:17:52 2 bo[30-31]
4113 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:18:01 2 bo[28-29]
4112 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:18:16 2 bo[26-27]
4111 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:18:27 2 bo[02-03]
4133 batch 80_nf5.5 ychuang R 7:13:43 1 bo01
4141 batch ccc xliang06 R 3:49:10 20 bo[05-08,10-25]
4137 hima 78_n9E5_ ychuang R 6:44:10 1 hi01
4136 hima 78_n9E5_ ychuang R 6:47:10 1 hi01
4135 hima 78_n9E5_ ychuang R 6:54:52 1 hi01
4134 hima 78_n9E5_ ychuang R 6:59:18 1 hi01
You can also limit this to just jobs under a particular username (like your own username, or someone else) with the -u flag,
13 [bora] squeue -u pmcardle
JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
4114 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:21:29 2 bo[30-31]
4113 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:21:38 2 bo[28-29]
4112 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:21:53 2 bo[26-27]
4111 batch run_2 pmcardle R 21:22:04 2 bo[02-03]
This command lists:
-
Job ID: The unique ID given to our job
-
Name: The name of the job
-
User: The username who launched the job
-
Time: Time elapsed on the job
-
Nodes / Nodelist: Number of nodes reserved and their number
Slurm: Deleting a job
You may want to delete a job before its walltime limit. Find the job ID (using squeue) and run scancel [JOB ID]. You should see Terminated whcih indicates the job has been successfully deleted.
Torque: qstat
For good measure, let’s cover the equivalents on Torque. Running qstat from your terminal will give you a table with statistics about all of the jobs currently running on the sub-cluster you are logged into. The output of this command will look like:
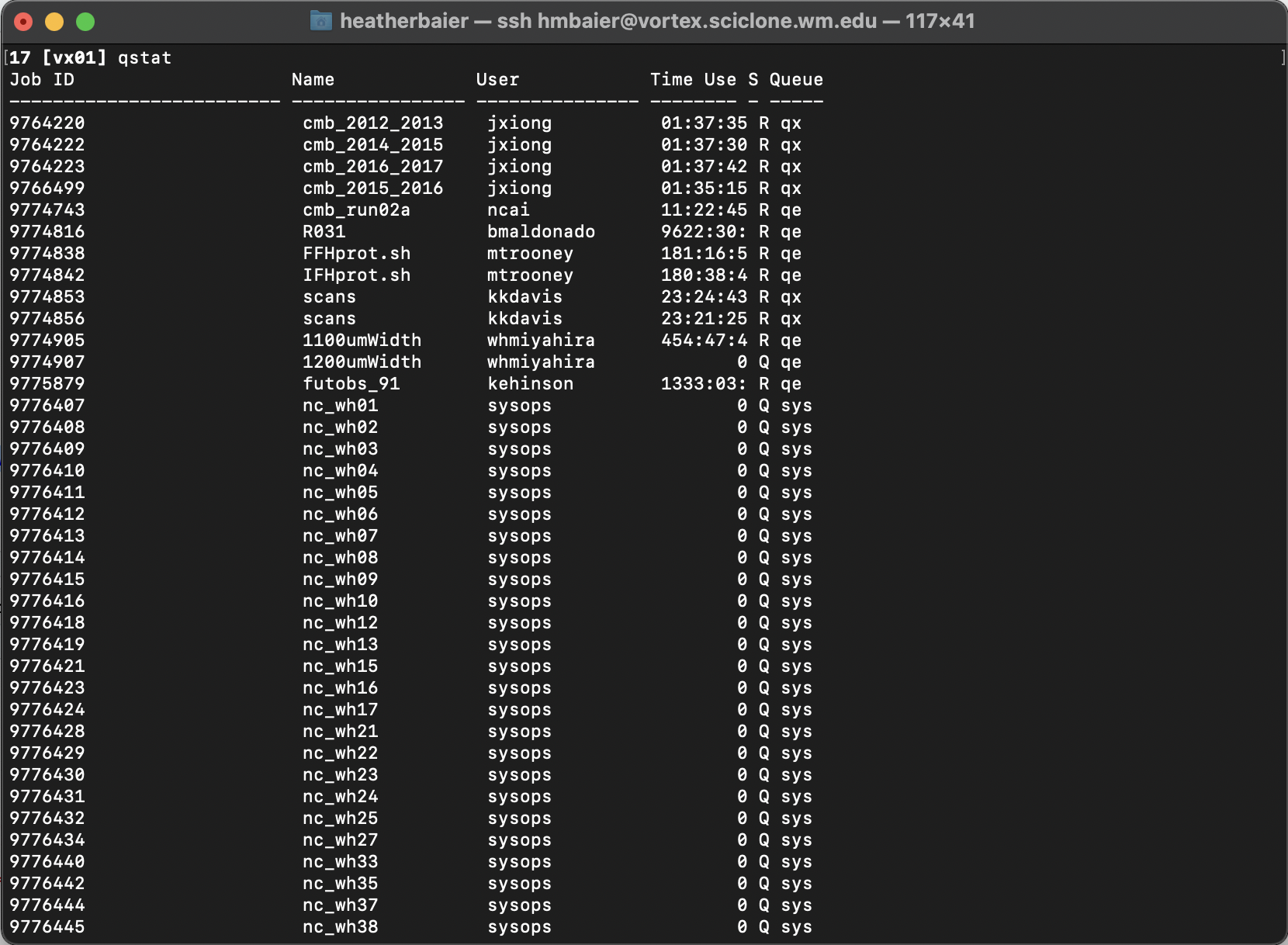
To limit this to a particular username, we can again use the -u flag qstat -u [USERNAME]. Or equivalently, the HPC has prepopulated all users’ .bashrc file with the alias qsu for qstat -u, so you can just do
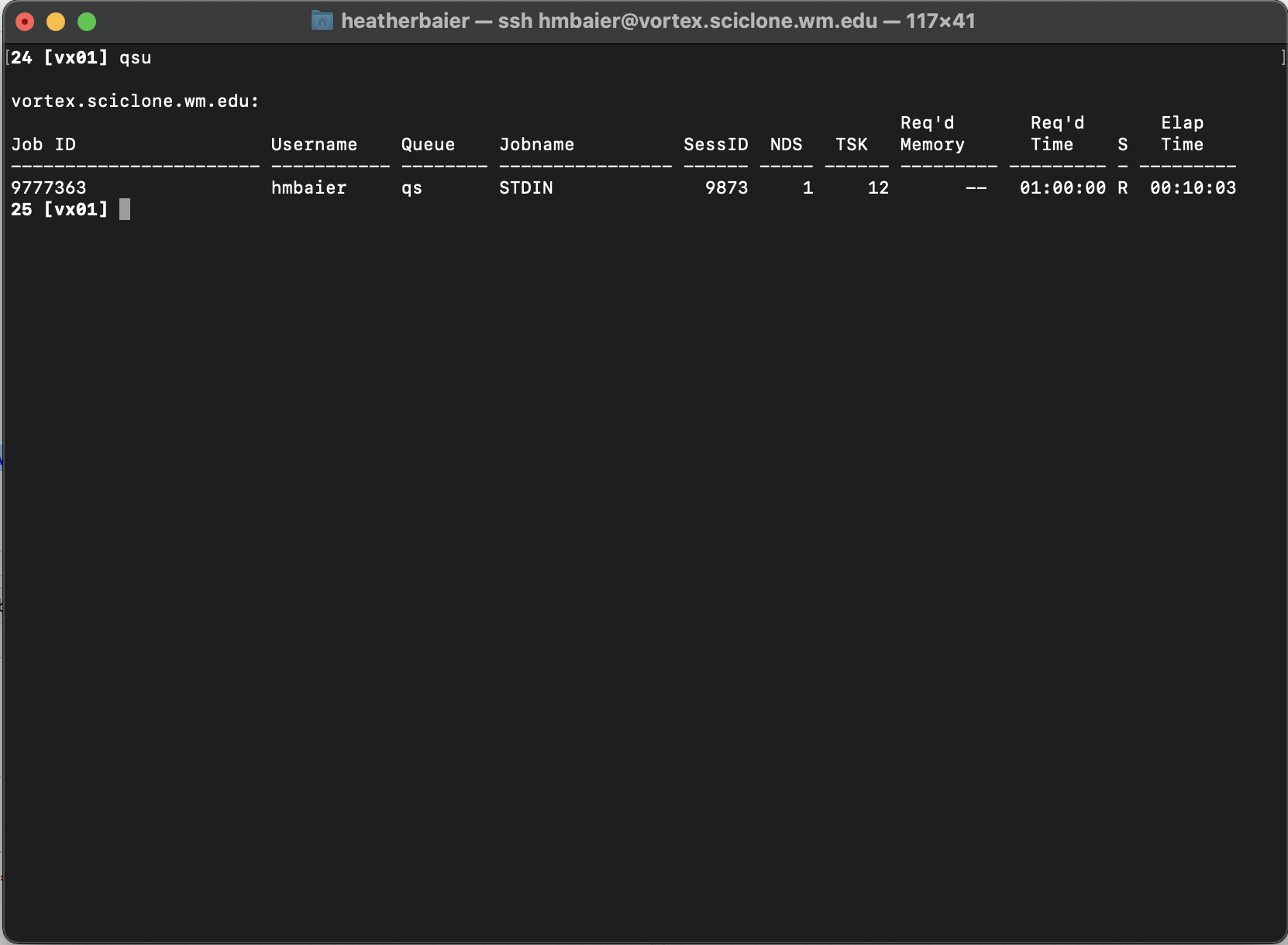
What does this table tell us?
Job ID: The unique ID given to our job
Username: The user who launched the job
NDS: Number of nodes reserved
TSK: Number of total processors reserved
Req’d Time: Amount of walltime requested
Elap Time: How long the job has been running for. If the job is in the queue and waiting to be launched, this line will look like
-----------
Torque: Deleting Jobs
If for any reason you decide that you want to cancel a job before it has reach it’s walltime limit, find the job ID (using either of the two methods in the previous page) and run qdel [JOB ID]
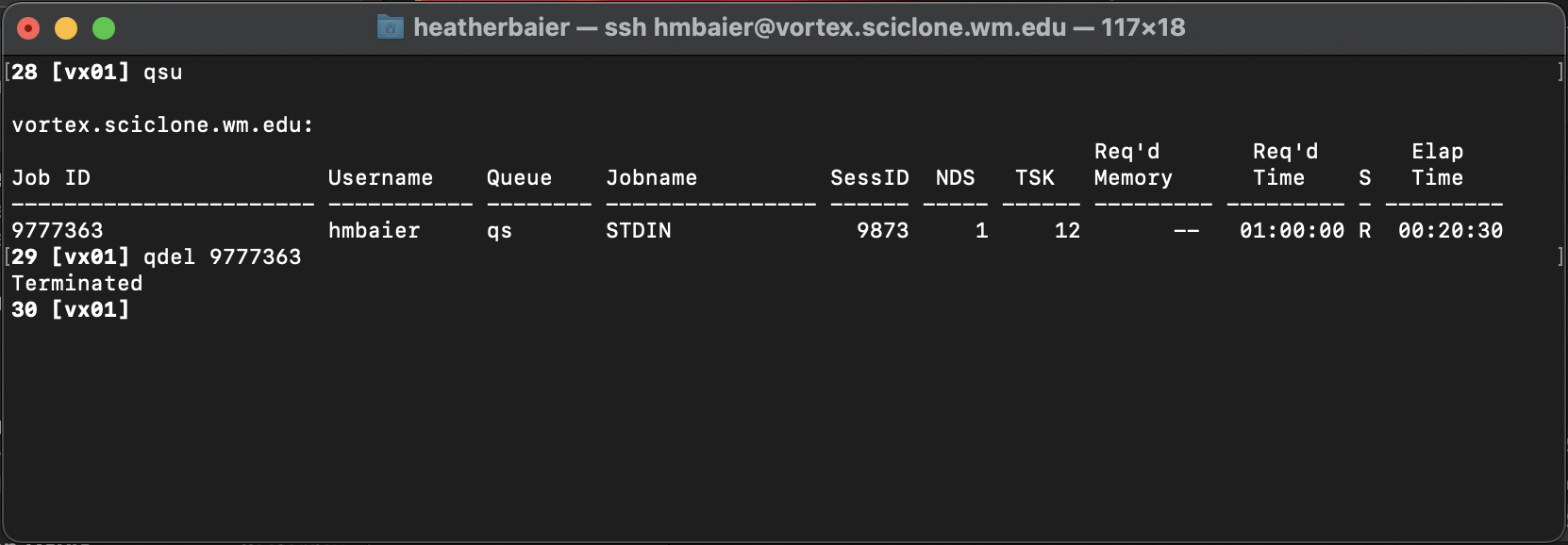
You should see Terminated, which indicates that the job has been successfully deleted.
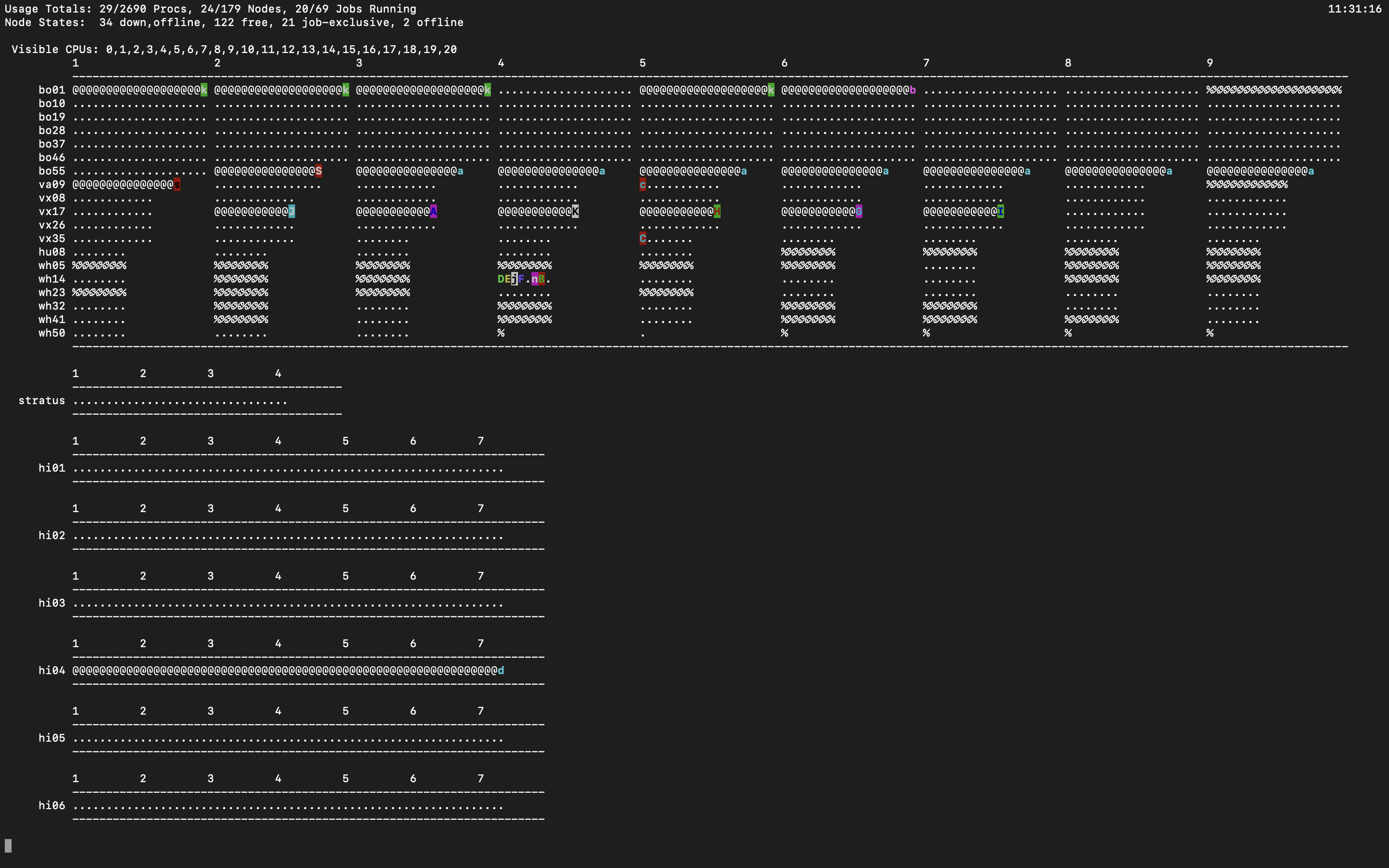
PBSTOP
Torque also had a utility called PBSTOP (a modification of the base TOP command) that gave a very nice overview of activity on the cluster. We’re not aware of an equivalent yet on Slurm, but for historical reference this is what PBSTOP output looked like: